Cisco GLBP Protocol
Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) is one of First Hop Redundancy Protocol (FHRP) which provides redundancy like other First Hop Redundancy Protocol, also provides load Balancing. It is a Cisco proprietary protocol which can perform both functions. It provides load Balancing over multiple routers using single virtual IP address and multiple virtual Mac address. GLBP terms :
- Virtual IP address : An IP address is assigned as a virtual IP address from the local subnet which is configured as a default gateway for all the local hosts.
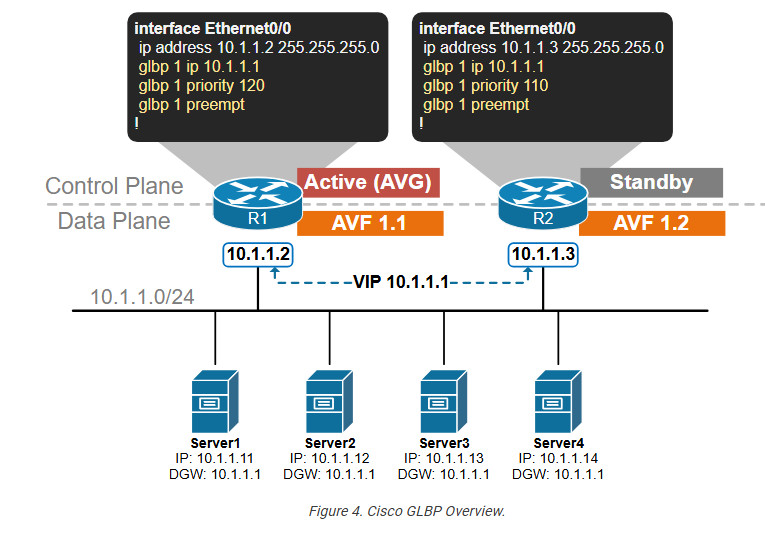
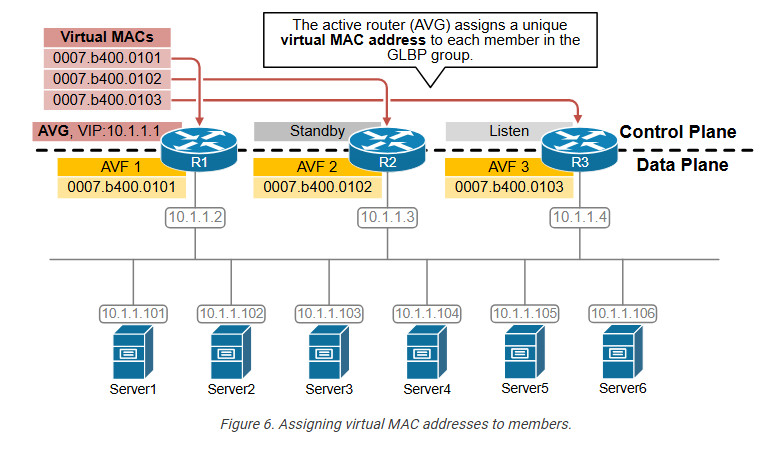
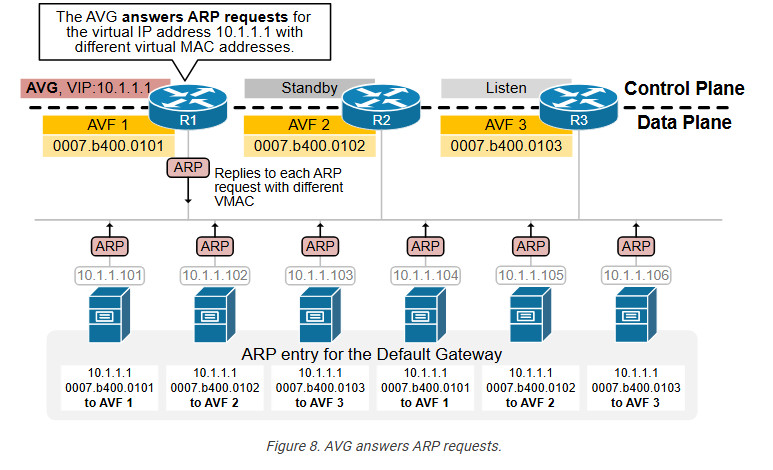
- Actual Virtual Gateway (AVG) : It is one of the router operating GLBP in a single group which is responsible for assigning virtual Mac address for each member in the group and for responding of the ARP request coming from the devices. The AVG has the highest priority value or IP address in the group.
- Actual Virtual forwarder (AVF) : These are the routers including the AVG in a single GLBP group. These are actually responsible for forwarding the data after they are assigned by the AVG for the task. If in case AVG goes down, one of the AVFs can become the AVG.
- Preempt : It is a state in which the one of the AVF will become the AVG router (when the AVG router goes down). Also, when the AVG router comes up again, it will become the AVG router as it’s priority is still higher (assumed).
- Object tracking : GLBP uses a weighting scheme to determine the forwarding capacity of each router in the GLBP group. GLBP tracks interface and adjusts it’s weighting i.e if the tracked interface goes down then it reduces by certain value (according to the configuration).
GLBP concepts :
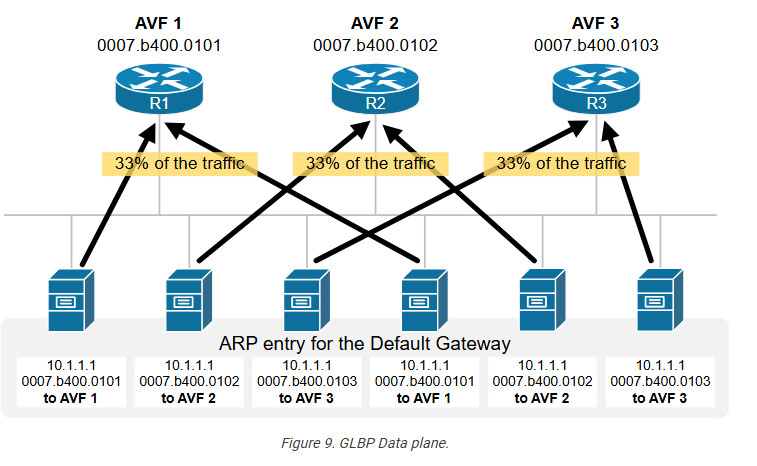
The Actual Virtual Gateway (AVG) provides virtual Mac addresses to all the other routers operating GLBP of the same group. The remaining routers are Actual Virtual Forwarder (AVF). When an ARP request comes from subnet device to know the Mac address of the virtual IP address, one of the virtual Mac addresses is provided by the AVG. AVG will provide the virtual Mac address by using Round Robin algorithm or other algorithms that have been applied. In this way, all devices running GLBP are used to forward traffic. GLBP virtual Mac address Assignment : When a subnet device (host) wants to send traffic, it requests a Mac address for the virtual IP (gateway) by sending an ARP request. In response to the ARP request, AVG will provide one of the virtual Mac address (provided to AVF by AVG). Virtual Gateway Redundancy : To detect a gateway failure, GLBP members communicate with each other through hello messages, sent in every 3-seconds to the multicast address
224.0.0.102. If AVG fails, then the AVF having highest priority will become the AVG i.e responsible for providing the Mac address of AVFs. Virtual forwarder Redundancy : Just like in HSRP, if one of the AVF fails then the other AVF in the same GLBP group will take the responsibility of forwarding the packets. There can be maximum 4 routers in a GLBP group.
Comparison between HSRP Vs VRRP Vs GLBP
Now let’s move to the main purpose of this article: To see similarities and differences between the 3 protocols. I’ll just state briefly some comparison points below and then use a table to compare more features.
- HSRP and VRRP are very similar. Both have one active and one standby router at any given time.
- GLBP is the only one which provides load balancing of traffic among the devices in the group.
- HSRP and GLBP are Cisco proprietary.
- VRRP is an IETF standard (RFC 3768) so it is supported by all router vendors.
- If you have a mixed vendor environment (e.g Cisco, Juniper etc) than its better to use VRRP.
- All protocols support more than 2 routers in a group.
- All protocols support tracking. This means that you can track an interface of the router (or other network conditions) and if something goes wrong (e.g interface goes down or a destination tracked host does not respond) then a failover action is triggered.
- HSRP and GLBP support IPv6. The original VRRP does not support IPv6 but you need a special version of VRRPv3 for this
GLBP load Balancing :
GLBP uses 3 algorithm for load Balancing –
- Round-Robin : AVG will assign the virtual Mac addresses serial wise, like first virtual Mac address is assigned to AVF1, then to AVF2 etc.
- Host-dependent : If particular host needs specific virtual Mac address every time then specific AVF is assigned to the hosts by the AVG.
- Weighted : The load will be distributed according to the requirement i.e assigning virtual Mac address in proportions. If we want some AVFs to handle more traffic than other, then change the weight.
Basic Configuration Of GLBP
GLBP Configuration
------------------
R1
interface Ethernet0/1
description LAN Interface of Primary Router
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
glbp 1 ip 192.168.1.254 <—- Create GLBP Group 1 and assign Virtual IP
glbp 1 priority 101 <—- Assign priority above 100 to make this the primary router
glbp 1 preempt <—- Makes router active if it has higher priority
glbp 1 load-balancing round-robin <—- Configure round-robin balancing of traffic
R2
interface Ethernet0/1
description LAN Interface of Secondary Router
ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
glbp 1 ip 192.168.1.254 <—- Create GLBP Group 1 and assign Virtual IP
glbp 1 preempt <—- Makes router active if it has higher priority
glbp 1 load-balancing round-robin <—- Configure round-robin balancing of traffic
Additional Commnd
.................
show glbp brief
show glbp
Timers – The default hello timer is 3 seconds. The default hold timer is 10 seconds.
R1(config-if)#glbp 10 timers ?
..............................
<1-60> Hello interval in seconds
msec Specify hello interval in milliseconds
redirect Specify timeout values for failed forwarders
Authentication – A router will ignore incoming GLBP packets from routers that
do not have the same
authentication configuration for a GLBP group.
R1(config-if)#glbp 10 authentication ?
......................................
md5 MD5 authentication
text Plain text authentication
By default, GLBP will load balance traffic using the round-robin method.
But we can change it by using the following command:
R1(config-if)#glbp 10 load-balancing ?
.......................................
host-dependent Load balance equally, source MAC determines forwarder choice
round-robin Load balance equally using each forwarder in turn
weighted Load balance in proportion to forwarder weighting
Let’s try changing it from round-robin to weighted
..................................................
R1(config-if)#glbp 10 load-balancing weighted
R1(config-if)#glbp 10 weighting 50
For verification, let’s use the ‘show glbp’ command
...................................................
R1#sh glbp | inc weight
Load balancing: weighted
Active is local, weighting 150
Active is 10.10.10.2 (primary), weighting 100 (expires in 11.424 sec)
Interface Tracking For ISP Link Router s0/0 Port
track 10 interface s0/0 line-protocol
show track
interface fa0/0
glbp 1 weighting track 10 decrement 10
glbp 1 weighting 120
hostname router-A
!
track 1 interface Serial0/0 line-protocol
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
glbp 10 ip 192.168.10.254
glbp 10 priority 255
glbp 10 weighting track 1 decrement 100
!
hostname router-B
!
track 1 interface Serial0/0 line-protocol
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.10.2 255.255.255.0
glbp 10 ip 192.168.10.254
glbp 10 priority 254
glbp 10 weighting track 1 decrement 100
!
COMPLETE GLBP CONFIGURATION (With Weight & Authentication)
----------------------------------------------------------
R1
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.10.2 255.255.255.0
glbp 10 ip 192.168.10.1
glbp 10 priority 120
glbp 10 preempt
glbp 10 weighting 120 lower 90 upper 110
glbp 10 authentication md5 key-string GLBPsecure
R2
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.10.3 255.255.255.0
glbp 10 ip 192.168.10.1
glbp 10 priority 100
glbp 10 weighting 100 lower 80 upper 100
glbp 10 authentication md5 key-string GLBPsecure
Verification Commands
......................
show glbp
show glbp brief
show glbp interface
IP SLA Configuration For Tracking Wan interface
-----------------------------------------------
ip sla 10
icmp-echo 8.8.8.8 source-ip 192.168.1.250
frequency 5
timeout 2000
exit
ip sla schedule 10 start-time now life forever
track 10 rtr 10
exit
interface fa0/0
glbp 10 weighting 110 lower 85 upper 105
glbp 10 weighting track 12 decrement 30
show glbp | include Active
show track
..........
Response Time Reporter 10 state
State is Up
1 change, last change 00:01:57
Latest operation return code: OK
Latest RTT (millisecs) 48
HSRP Configration
.................
interface fa0/1 (Lan interface)
stanby 1 ip 10.10.10.250 (Virtual IP Gateway Configration)
standby 1 preempt
stanby 1 priyority 105