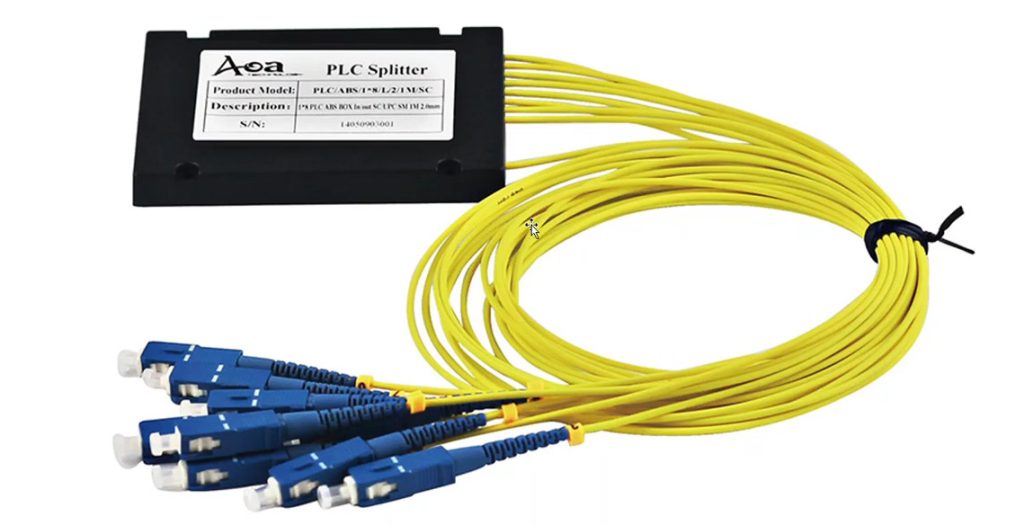
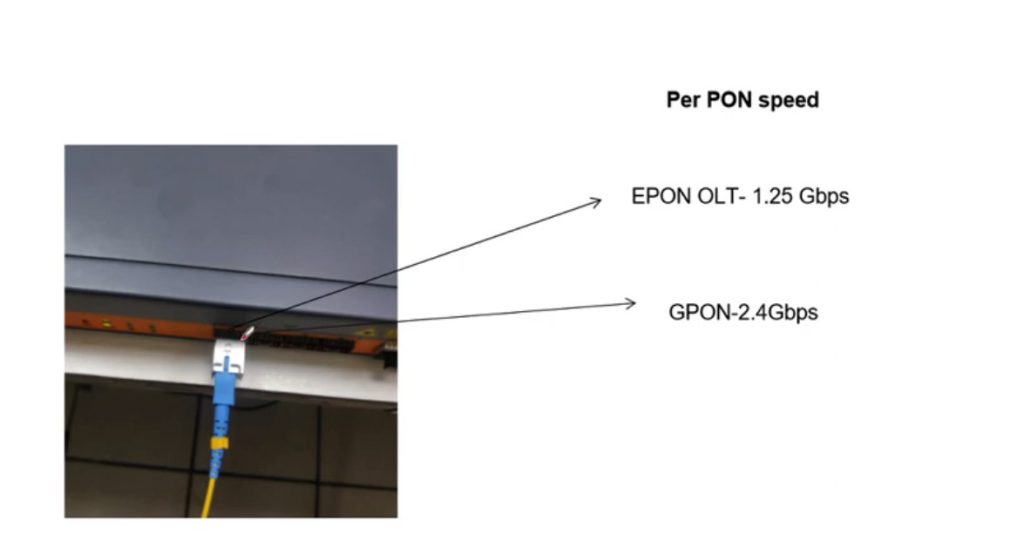
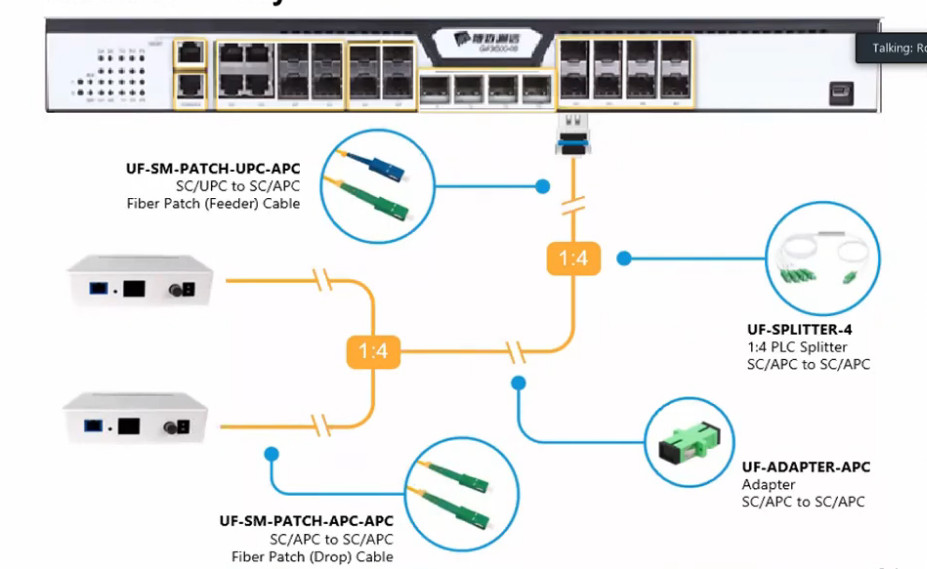
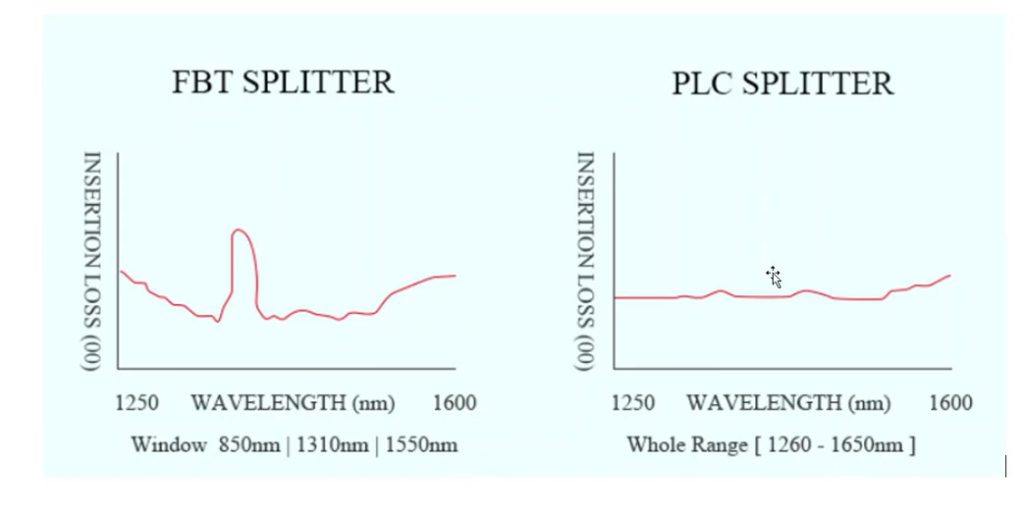
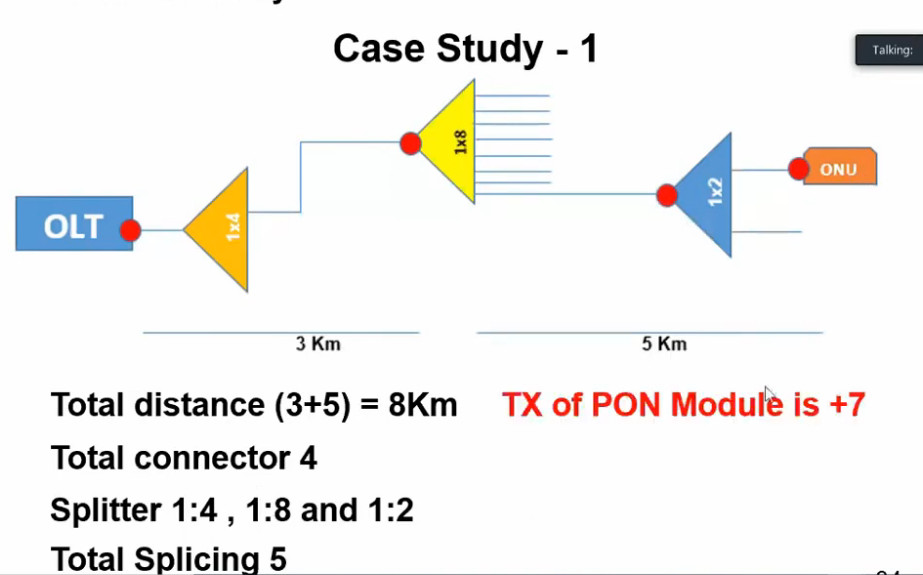
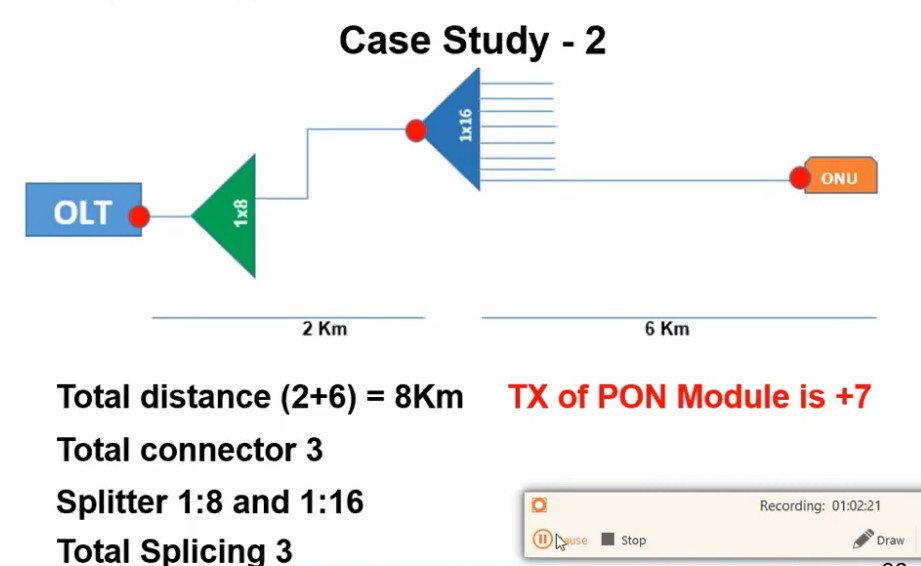
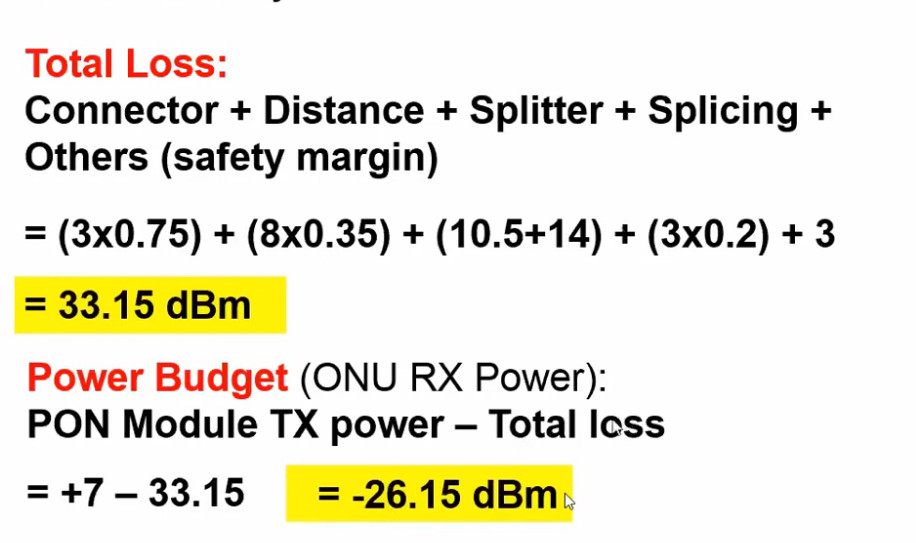
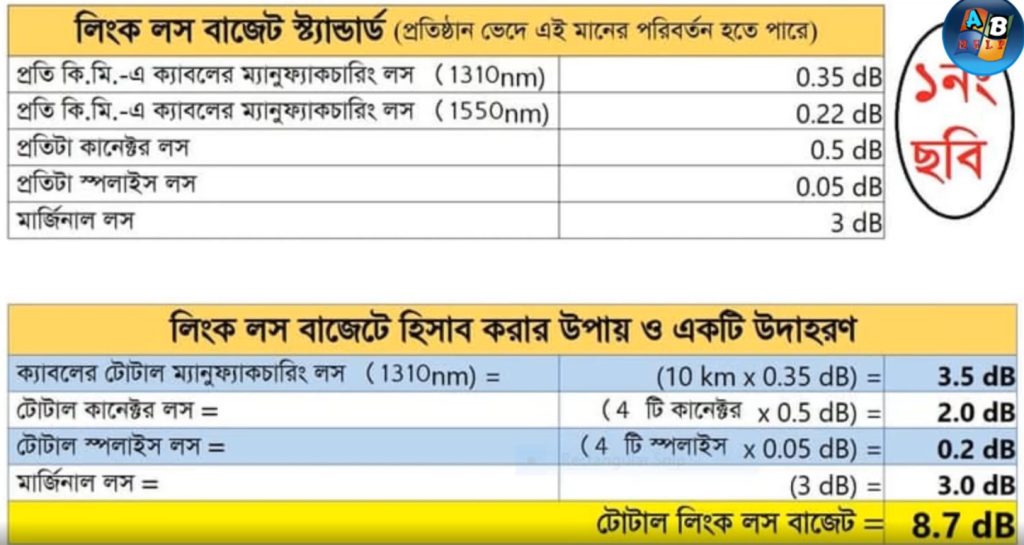
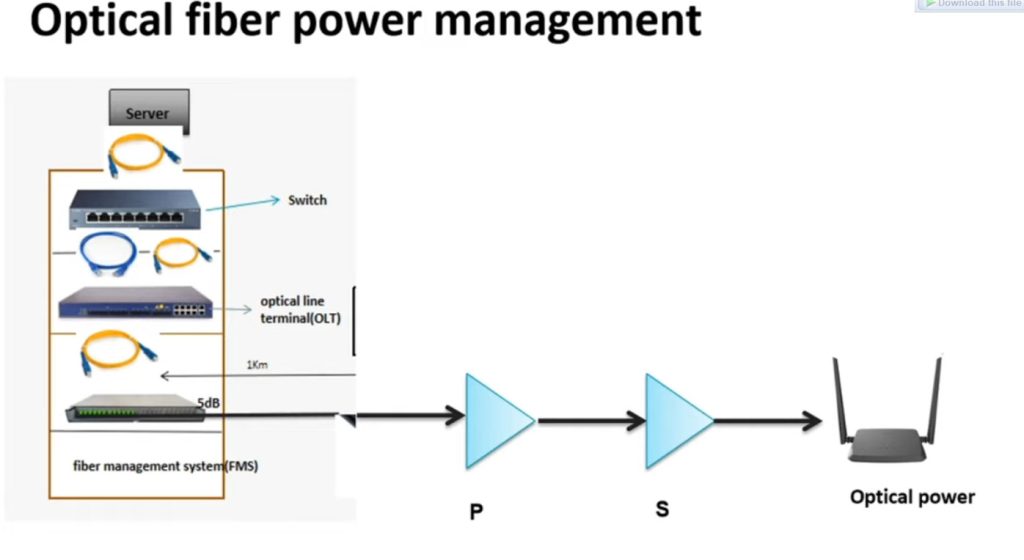
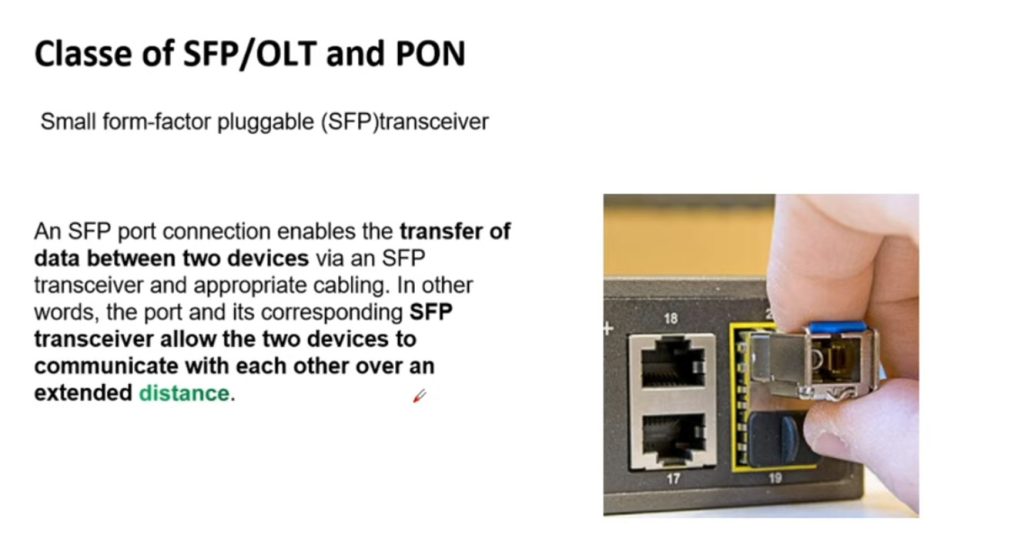
Optical Power Budget & Cable Deployment
Single-Mode Fiber (SMF):
- 850 nm: This wavelength is used in short-range applications like local area networks (LANs). It experiences higher loss compared to 1310 nm and 1550 nm.
- 1310 nm: Widely used for longer-distance transmissions. The attenuation is lower than at 850 nm, and this wavelength is often used for medium-distance connections.
- 1550 nm: This is the lowest loss wavelength for single-mode fiber, making it ideal for long-haul fiber optic communication systems like telecom and fiber-optic backbone links. It’s commonly used for FTTH (Fiber-to-the-Home) and long-distance communication. It has minimal attenuation and is the most efficient for long-distance signals.
Multi-Mode Fiber (MMF):
- 850 nm: This wavelength is primarily used for shorter-distance communication, such as within buildings or campuses. Multi-mode fiber has significantly higher attenuation than single-mode fiber at 850 nm, which is why it’s not used for long-distance transmission.
- 1310 nm: Used in longer-distance multi-mode applications. However, MMF still has higher attenuation compared to SMF, which limits its application in long-haul systems.