Difference between
Fiber optic cable and Copper wire
In computer network, cables are the medium through which data transfer from one computer to another. There are several types of computer cables available. The type of cable chosen for a network is related to the network topology, protocol, and size. Fiber optic cables and copper wires are the two primary types of cables used in networks. The selection of fiber optic cables over copper wires or vice versa depends on factors such as bandwidth, distance, and cost of transmission. Fiber optic cables transmit data using light waves, enabling higher speeds and cover long distance. They are ideal for long-distance communication and high-speed internet, but they are more expensive to install. While copper uses electrical currents which are cheaper and more affordable to install. In this article, we will see difference between Fiber optic cable and Copper wire in detail.
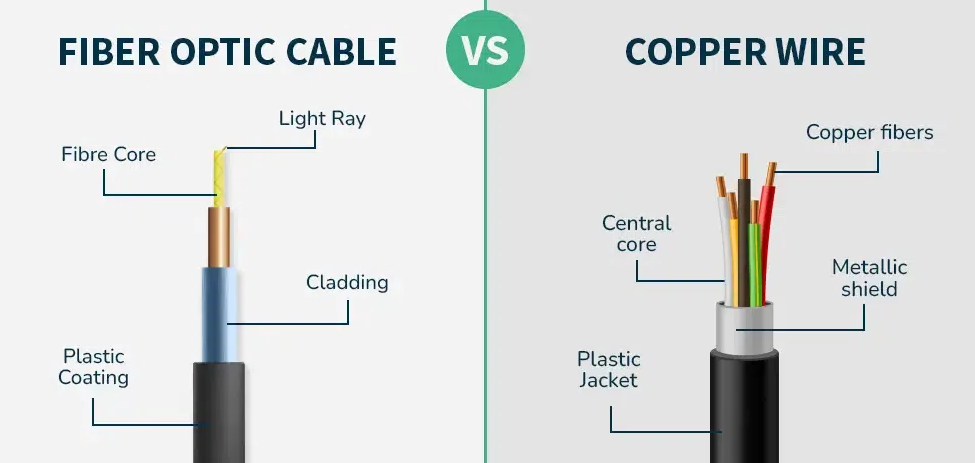





What is Fiber Optic Cable?
Fiber Optic Cable is also known as the Optical Fiber Cable. It is made up of plastic or glass. It transmits signals in the form of light. There are 3 basic components of the optical transmission system which are as follows:
- Light source
- Transmission media (fiber optics)
- Detector
Characteristic of Fiber Optic Cable
One of the most important characteristics of fiber optic cable is its capacity for extremely high bandwidth. Fiber optics facilitate very swift transmission of a huge amount of information by the use of wires, without the wires suffering from collapse over long distances. Fiber optics do not make use of electrical signals and hence are able to transmit data without being affected by other electrical devices in the region.
Advantages of Fiber optic cables
- High bandwidth: Fiber optic cables have a much higher bandwidth than copper wires, which means they can carry more data at faster speeds.
- Long distance: Fiber optic cables can transmit data over long distances without signal loss. This makes them ideal for long distance communication.
- Immunity to electromagnetic interference: Fiber optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference, which can be a significant problem for copper wires.
- Security: Fiber optic cables are much more difficult to tap into or intercept than copper wires, making them more secure for sensitive data transmission.
Disadvantages of Fiber Optic Cables
- Cost: Fiber optic cables are generally more expensive than copper wires, which can be a significant factor in some applications.
- Fragility: Fiber optic cables are more fragile than copper wires and can be damaged easily if not handled carefully.
- Limited compatibility: Fiber optic cables are not always compatible with older network equipment and may require costly upgrades.
What is Copper Wire?
Copper wire is a type of electrical conductor made from copper, widely used in various forms of electrical wiring due to its excellent conductivity. In computer networking, copper wires are typically used to transmit data through electrical signals. It transmits data in the form of electronic signals. It is the single solid conductor.
Characteristics of Copper Wire
The features of copper wire include strength, relatively low cost, and the ability to work with many network equipment types. They are the most common network wiring in the short-distance data connections as they suffer attenuation when used for longer stretches. Again, copper wire has the merit of being capable of carrying both data and electrical signals which makes it applicable in more than one field. On the other hand, copper wires are also affected by electromagnetic disturbances and their bandwidth is significantly lower than that of fiber optic wires.
Advantages of Copper Wires
- Low cost: Copper wires are generally less expensive than fiber optic cables, which can make them more cost-effective for some applications.
- Easy to install: Copper wires are easy to install and work with, which can make them a more convenient choice for some applications.
- Compatibility: Copper wires are compatible with a wide range of network equipment, making them a versatile choice.
- Durability: Copper wires are more durable than fiber optic cables and can withstand more physical abuse.
Disadvantages of Copper Wires
- Limited bandwidth: Copper wires have a lower bandwidth than fiber optic cables, which means they can carry less data at slower speeds.
- Signal loss: Copper wires are more susceptible to signal loss and degradation over long distances, which can limit their usefulness in certain applications.
- Electromagnetic interference: Copper wires are susceptible to electromagnetic interference, which can cause signal distortion and other problems.
- Security: Copper wires are more vulnerable to interception and eavesdropping than fiber optic cables.
Similarities between Fiber Optic Cables and Copper Wires
- Both are used for data transmission: Both fiber optic cables and copper wires are used to transmit data in various applications such as telecommunications, networking, and broadcasting.
- Both require connectors: Both fiber optic cables and copper wires require connectors to connect to devices and other cables.
- Both can be used for power transmission: Copper wires can be used for power transmission, and fiber optic cables can be used to power some devices using light.
- Both have different types: Both fiber optic cables and copper wires have different types designed for specific applications, such as single-mode and multi-mode fiber optic cables and stranded and solid copper wires.
- Both require proper installation and maintenance: Both fiber optic cables and copper wires require proper installation and maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Difference between Fiber Optic Cable and Copper Wire
| Basis | Fiber Optic Cable | Copper Wire |
|---|---|---|
| Data Carrier | It carries data in the form of light. | It carries data in the form of electric signals. |
| Bandwidth | It offers higher bandwidth. | It offers lower bandwidth. |
| Structure | It is thin, lighter in weight, and smaller in size. | It is heavier and thicker. |
| Environment | It can be laid in different environments because it is more resistant to corrosive materials. | It cannot be laid in a different environment because it is more prone to corrosive materials. |
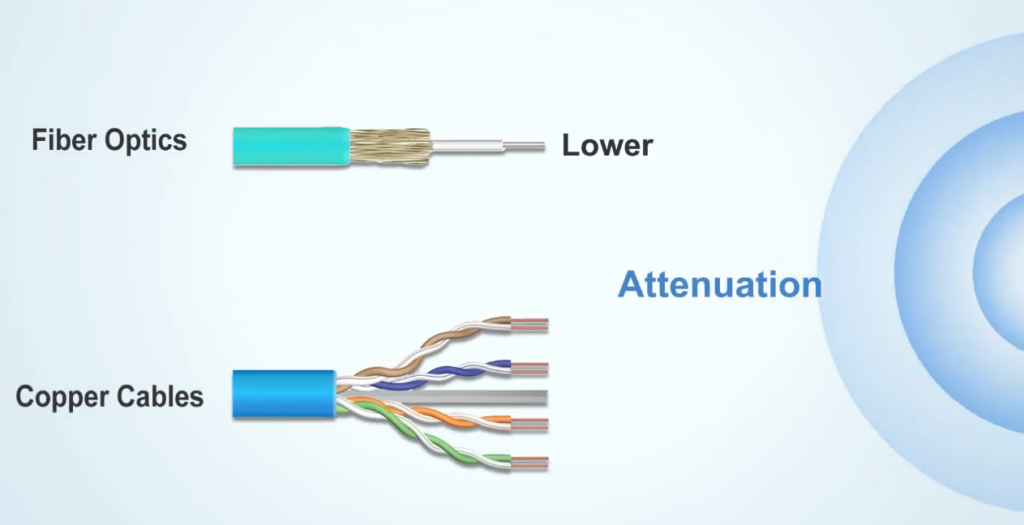
| Attenuation | Attenuation is very low. | Attenuation is high. |
| Interface | As this data travel in the form of light, they are not affected by the electrical and magnetic interfaces. | As in this data travel in the form of electric signals, they are affected by the electrical and magnetic interfaces. |
| Security | They provide security against the wiretappers, because there is no leakage of light and are difficult to tap. | They do not provide security against the wiretappers, because there is leakage of signals, and are easy to tap. |
| Cross-talk problem | There is no such kind of problem. | These are prevalent this problem. |
| Effect on charge carriers | In this charge carriers are photons, they do not carry any charge, so they do not get affected. | In this charge carriers are electrons, they carry a negative charge, so they get affected when they move in a wire. |
| Break-ability | They are easily breakable. | They cannot be easily broken. |
| Installation Cost | Installation Cost is high. | Installation Cost is less. |
| Bandwidth Size | It is a bandwidth size 60Tps. | It is a bandwidth size 10Gbps. |
| Width | Fiber Optic width around 4lbs/1000 ft. | Copper wire width around 39lbs/1000ft. |
Comparison: Fiber Optic vs. Copper Cables
To make an informed decision about which cable type is best for your data center, it’s essential to compare fiber optic and copper cables across several key factors.
Data Transmission Speed and Bandwidth
Fiber optic cables significantly outperform copper cables in terms of data transmission speed and bandwidth. While copper cables can support speeds up to 10 Gbps over short distances, fiber optic cables can achieve speeds of 100 Gbps and beyond over much longer distances. The boundaries continue to be pushed in 2024 with some fiber optic cables transmission speeds reaching 800 Gbps and whispers of a mind-boggling 1.6 Tbps in the future.
Distance Limitations
Copper cables experience signal degradation over relatively short distances, typically limiting their effective range to around 100 meters for high-speed applications. Fiber optic cables, on the other hand, can transmit data over distances of several kilometers without the need for signal regeneration.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Susceptibility
Copper cables are susceptible to EMI, which can cause signal distortion and data loss. Fiber optic cables, being immune to EMI, provide more reliable data transmission in environments with high electromagnetic activity.
Power Consumption and Heat Generation
Fiber optic cables consume less power and generate less heat compared to copper cables, contributing to improved energy efficiency in data centers.
Cost Considerations
While fiber optic cables have a higher initial cost, their superior performance and longevity often result in lower total cost of ownership over time. Copper cables may be more cost-effective for smaller installations or short-distance applications.
Durability and Lifespan
Properly installed fiber optic cables typically have a longer lifespan than copper cables and are less likely to require replacement due to technological obsolescence.
Fiber Optic vs Copper: Tale of Two Cables | ||
Feature | Fiber Optic Cables | Copper Cables |
Data Transmissions | Up to 800 Gbps (future: 1.6 Tbps) | Up to 10 Gbps (limited distance) |
Distance Limitations | Several kilometers | Up to 100 meters (high-speed applications) |
EMI Susceptibility | Immune | Susceptible |
Power Consumption & Heat Generation | Lower | Higher |
Cost Considerations | Higher initial cost, lower TCO (long-term) | Lower initial cost, may be higher TCO (short-term) |
Durability and Lifespan | Longer lifespan | Shorter Lifespan |
Use Cases: When to Choose Fiber or Copper Cables
Understanding the appropriate use cases for each cable type can help data center managers make the right choice for their specific needs.
Scenarios where copper cables are preferred:
- Short-distance connections (less than 100 meters).
- Legacy system compatibility.
- Power over Ethernet (PoE) applications.
- Budget-constrained.
- Projects with lower bandwidth requirements.
Scenarios where fiber optic cables are preferred:
- Long-distance connections (over 100 meters).
- High-bandwidth applications (40Gbps, 100Gbps, and beyond).
- Future proofing for scalability.
- Environments with high EMI.
- Data centers that prioritize energy efficiency.
While fiber optic cables are increasingly becoming the standard for new data center installations, copper cables still have their place in certain scenarios. The choice ultimately depends on your specific requirements and future growth plans.
Future Trends in Data Center Connectivity
As data center requirements continue to evolve, it’s crucial to consider future trends when making infrastructure decisions. The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is significantly impacting data center connectivity needs, adding new dimensions to the already complex landscape.
Evolving data center requirements – and what it might mean for your cabling decisions – include:
- Increasing Bandwidth and Lower Latency: The demand for higher bandwidth and lower latency continues to grow, driven by data-intensive applications and real-time processing needs. This trend is further accelerated by AI and ML workloads, which require massive data transfers and rapid communication between compute nodes.
- AI-Driven Connectivity Demands:
- AI Training: Large-scale AI model training requires enormous amounts of data to be moved between storage and compute resources. This demands ultra-high-bandwidth connections, often in the range of 400Gbps to 800Gbps, with future needs potentially reaching terabit speeds.
- AI Inference: While less bandwidth-intensive than training, AI inference still requires low-latency, high-throughput connections to deliver real-time results.
- Distributed AI: As AI workloads become more distributed across edge, core, and cloud environments, the need for flexible, high-performance connectivity between these locations increases.
- AI Training: Large-scale AI model training requires enormous amounts of data to be moved between storage and compute resources. This demands ultra-high-bandwidth connections, often in the range of 400Gbps to 800Gbps, with future needs potentially reaching terabit speeds.
- Growth of Edge Computing: The proliferation of IoT devices and the need for real-time processing are driving the growth of edge computing. This trend requires robust, low-latency connections between edge locations and central data centers, often favoring fiber optic solutions.
- Focus on Energy Efficiency and Sustainability: As data centers grow larger and more power-hungry, there’s an increased focus on energy efficiency. This trend favors technologies that offer high performance with lower power consumption, such as advanced fiber optic solutions.
- Scalability and Flexibility: The unpredictable nature of AI workloads and rapid technological advancements require data center infrastructures to be highly scalable and flexible, able to adapt quickly to changing demands.
To meet these evolving requirements and future trends, the cabling industry is responding with significant technological advancements. These innovations are designed to support the increasing demands for bandwidth, speed, and efficiency in data centers while addressing the specific needs of emerging technologies like AI and edge computing.
Technological Advancements for Cables of All Types
As data center infrastructure undergoes rapid transformation, cable technology is evolving to keep pace.
Both fiber optic and copper cables are seeing improvements that enhance their capabilities and expand their potential applications.
On one hand you have higher-capacity fiber optic cables – both multi-core and multi-mode fibers – capable of supporting terabit-per-second speeds.
Wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) technology is also improving which will allow existing fibers to increase their data-carrying capacity.
On the other hand, traditional copper cable technology continues to improve with the development of higher category cables (e.g., Category 8 and beyond). There are also advancements being made in signal processing and noise cancellation techniques that can extend the capabilities of copper cabling.
Even the connections are advancing with silicon photonics enabling more efficient, higher-density optical connections and the development of optical transceivers and switching technology to support the increasing bandwidth demands of AI workloads.
Explain 2
What is a Fiber Optic Cable?
Fiber optic cable is a type of cable that uses glass or plastic fibers to transmit data. The cable is made up of a core, which is the central part of the cable, and a cladding, which is a layer of material that surrounds the core. The cladding is designed to keep the light signal within the core, preventing it from escaping. The cable is then coated with a protective layer to prevent damage.

How do Fiber Optic Cables Work?
Fiber optic cables operate on the principle of total internal reflection. When data is transmitted, it is converted into light pulses. These pulses travel through the core of the fiber optic cable, constantly reflecting off the cladding layer due to the difference in refractive indices. This process ensures that the light stays confined within the core, allowing for efficient and high-speed data transmission.
Applications of the fiber optic cables include:
1.Telecommunications:Fiber cables are widely used in the telecommunications industry for long-distance communication. The high bandwidth and low signal loss make them ideal for transmitting voice, video, and data over vast distances.
2.Network Backbones: Fiber cables play a crucial role in providing high-speed Internet services to homes and businesses. The ability to transmit large amounts of data quickly and reliably makes them a preferred choice for broadband connections.
3.Data Centers: In data centers, where massive amounts of data are processed and transferred, fiber optic cables are the preferred medium. They offer high data transfer rates and are resistant to EMI, ensuring the integrity of critical data.
What is a Copper Cable?
Copper cable is a type of cable that uses copper wires to transmit data. Copper wires are made up of thin strands of copper that are twisted together to form a cable. The cable is then coated with a protective layer to prevent damage. Copper cables come in various forms, including twisted pair cables and coaxial cables, each serving specific purposes in networking.

How do Copper Cables Work?
Copper cables function by sending electrical signals through a conductor, typically made of copper or aluminum. In twisted pair cables, two insulated copper wires are twisted together, reducing electromagnetic interference. In coaxial cables, a central conductor is surrounded by an insulating layer, a metallic shield, and an outer insulating layer. The electrical signals travel along the central conductor, and the metallic shield helps prevent signal interference.
Applications of the copper cables include:
1.Local Area Networks (LANs):Copper cables are commonly used in LANs for connecting computers and devices within a confined geographical area. Ethernet cables, a type of twisted pair cable, are prevalent in this context.
2.Telephone Lines:Traditional telephone lines often use twisted pair copper cables for voice communication. Despite the rise of digital communication technologies, copper cables continue to play a role in telephony.
3.CCTV Systems: Coaxial cables are widely used in the CCTV systems to transmit unprocessed video signals from analog cameras. The shielding in coaxial cables helps maintain signal quality over longer distances. The coaxial cables can also be used with IP cameras when combined with a signal converter in an Ethernet over Coax system. On the other hand, Ethernet cables are typically used to connect PoE IP cameras although they can be adapted for analog cameras with a video balun.
Differences between Fiber Optic Cables and Copper Wires
1.Speed and Bandwidth
One of the main differences between fiber optic cables and copper wires is their speed and bandwidth. Fiber optic cables can transmit data at much higher speeds than copper wires. While copper wires can transmit data at speeds up to 10 Gbps, fiber optic cables can transmit data at speeds up to 100 Gbps. Fiber optic cables also have a higher bandwidth than copper wires, meaning they can transmit more data at the same time.

2.Distance
Another difference between fiber optic cables and copper wires is their distance capabilities. Copper wires are limited in the distance they can transmit data, typically 100 meters. As the distance increases, the electrical signals in copper wires may weaken, requiring signal amplification or repeaters to maintain data integrity. Fiber optic cables, on the other hand, can transmit data over much longer distances. They can transmit data up to 40 kilometers without losing signal strength.
3.Power
Copper cables are widely employed for both data and power transmission. PoE enables the simultaneous transmission of data and electrical power over the same Ethernet cable, simplifying the setup of devices like IP cameras, phones, and access points. In addition to PoE, copper wires can be used to provide electrical power for various applications, such as electrical appliances, lighting, and low-voltage systems. Primarily designed for data transmission, fiber optic cables are not used for delivering power directly.

4.Signal Interference
Copper wires are susceptible to signal interference from other electronic devices, power lines, or radio frequency sources, leading to signal degradation and potential data corruption. In twisted pair copper cables, signals in adjacent pairs can interfere with each other, causing crosstalk and data errors. Fiber optic cables, on the other hand, do not generate electromagnetic fields, making them highly resistant to external interference. Moreover, they are resistant to environmental factors such as moisture, temperature fluctuations, and corrosive substances.
5.Security
Fiber optic cables are more secure than copper wires. Copper wires can be tapped into, allowing someone to intercept the data being transmitted. They are vulnerable to EMI and RFI, which can result in signal leakage and compromise the integrity of transmitted data. They may require additional security measures, such as encryption, to ensure data confidentiality. Fiber optic cables, on the other hand, are much more difficult to tap into. The light signal being transmitted through the cable cannot be intercepted without disrupting the signal. They are also less susceptible to signal degradation and data corruption, providing a higher level of security.
6.Installation and Cost
Fiber optic cables are more difficult to install than copper wires. The installation process for fiber optic cables requires specialized equipment and trained professionals. Copper wires, on the other hand, can be installed by anyone with basic knowledge of network cabling. In addition, copper wires are less expensive than fiber optic cables. While copper wires are relatively inexpensive, the cost of fiber optic cables is higher due to the complex manufacturing process and the cost of the materials used.
Here’s a summarized chart highlighting the key differences between fiber optic cables and copper wires across various aspects:

Conclusion
In conclusion, both fiber optic cables and copper wires have their advantages and disadvantages. Copper wires are less expensive and can transmit data and power simultaneously, while fiber optic cables have a higher bandwidth and transmit data over long distances. When choosing a cable for your network setup, it is important to consider your specific needs and requirements.
